
Everything You Need to Know About SAGA Protocol Airdrop, SAGA Airdrop Eligibility, SAGA Token Withdrawal
SAGA BLOCKCHAIN AND AIRDROP | Saga is a platform that introduces a completely new concept called Chainlet, which was recently announced by Binance as its 51st Launchpool project. So, what is Saga? Let’s find out right away!

Contents
What is Saga?
About Saga Protocol
Saga Protocol is not just a project providing blockchain building services for applications but also marks a breakthrough through the concept of “Chainlet” within its ecosystem. Unlike other projects, Saga not only creates independent blockchains but also serves as a comprehensive security source, known as Interchain Security.
Interchain Security is a unique mechanism where each blockchain or Chainlet in this case, becomes a security provider for other blockchains. This means that Chainlets not only benefit from running on the Cosmos SDK platform but also leverage the strength of validators from Saga to ensure block safety and validation. This distinguishes Saga Protocol in the blockchain community with its unique model and strong security integration from Cosmos.
Recently, Binance announced Saga as its 51st Launchpool project.
Binance Announces Listing of Saga (SAGA) on Launchpool
How does Saga work?
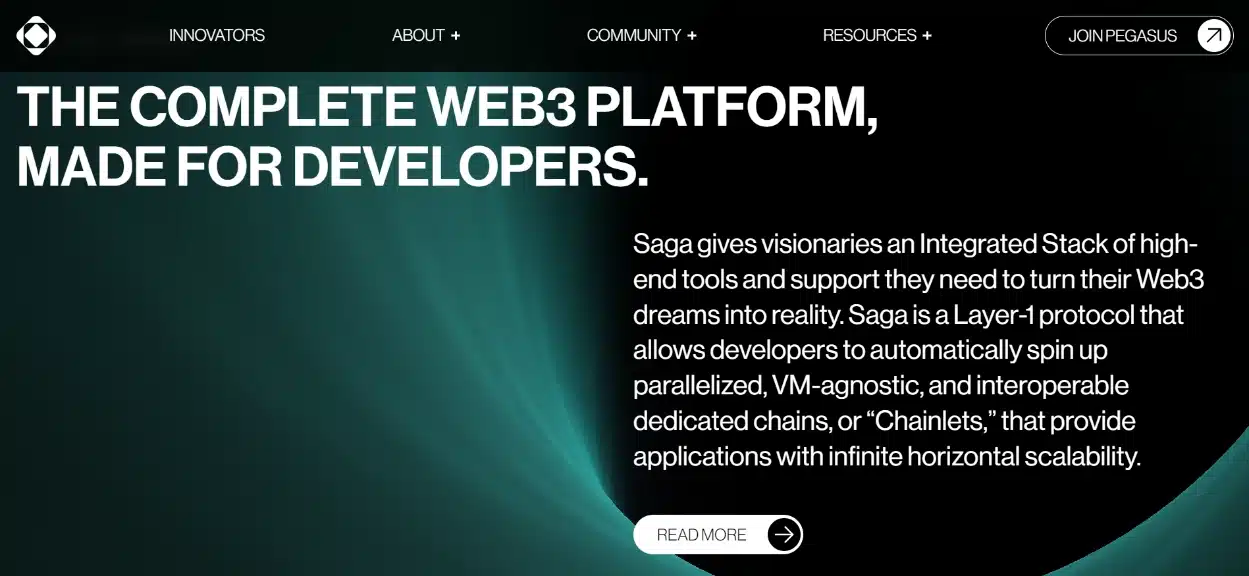
Saga is a Layer 1 blockchain protocol designed to enhance Web3 development efficiency. It introduces an innovative method for developers to automatically create separate blockchains, called Chainlets, customized for specific applications. These Chainlets run in parallel, promoting scalability and interaction while maintaining top-notch performance and security. Saga’s framework notably simplifies Web3 application development by providing a scalable, secure, and optimized infrastructure.
Key technical features of Saga include:
- Automatic Chainlet Generation: Developers can easily generate dedicated blockchains for their applications, ensuring scalability and customization.
- Cosmos Interchain Security (ICS): Chainlets inherit robust security directly from Saga’s Mainnet, thanks to shared validator services.
- Cosmos SDK Modules Compatibility: Supports a variety of virtual machines and SDK modules, allowing for flexible application development.
- Elastic Scalability: The architecture permits expansion in line with application demand, ensuring that blockspace never limits performance.
- SagaOS Integration: Offers a comprehensive stack for app development, including automated smart contract deployment, low and predictable fees, and fast asset interoperability.
Related: Everything you need to know about wormhole airdrop
What are Saga Chainlets?
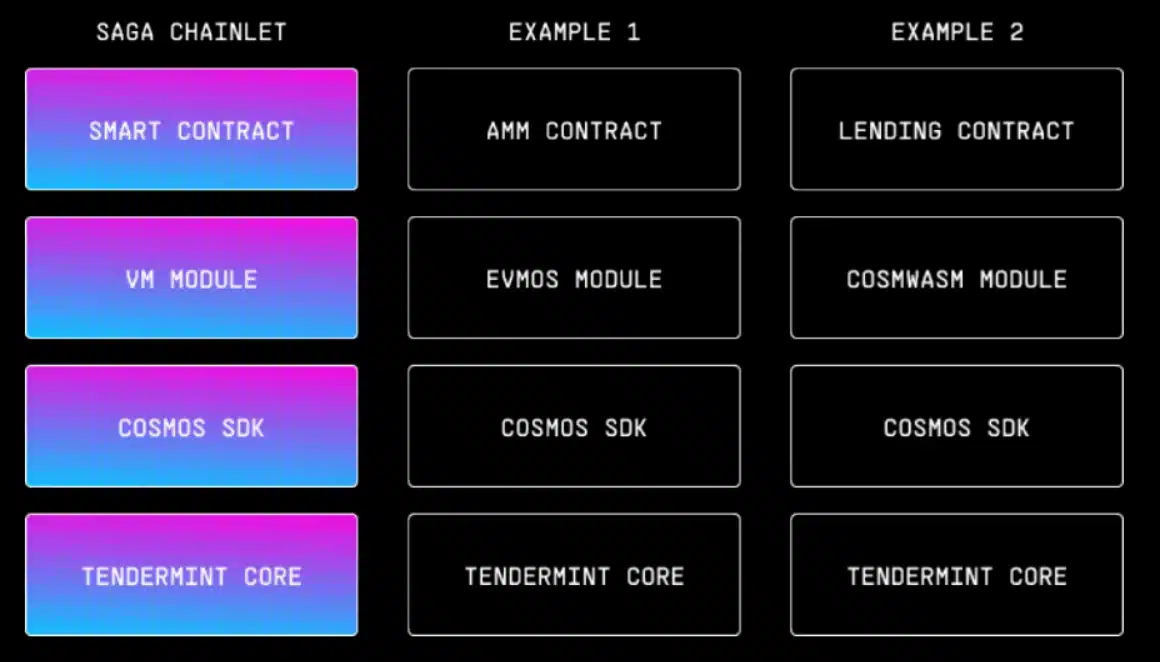
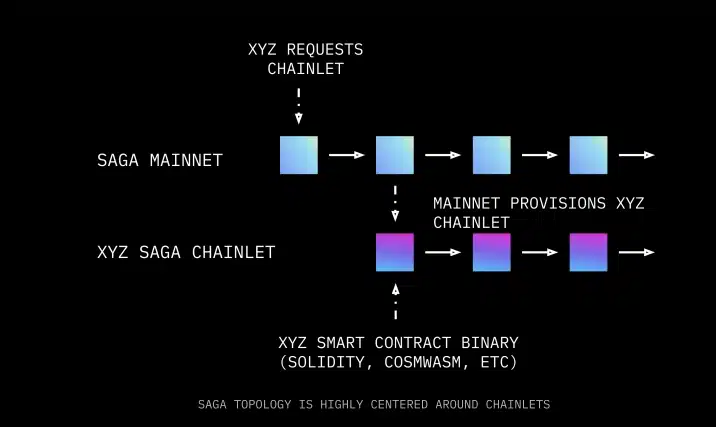
Saga Chainlets operate as independent blockchains customized for executing individual smart contracts, providing developers with their own deployment space. This setup not only brings predictability in transaction fees due to dedicated blockspace but also supports the use of various virtual machines, including the EVM, ensuring flexibility. Components of a Chainlet, such as its VM module and SDK, can be independently updated, offering adaptability without affecting the main network or other Chainlets.
A standout feature of Saga’s Chainlets is their dedicated validator sets, safeguarded by Saga’s shared security mechanism. This structure underpins the development of scalable, efficient Web3 applications by providing exclusive blockspace. It allows for tailoring Chainlets to meet specific needs across various execution environments, thereby amplifying scalability.
Each Chainlet has tools such as RPC endpoints for seamless integration and a Chainlet block explorer for real-time monitoring. Saga’s streamlined approach enables scalable, flexible blockchain application development.
Key Highlights of Saga:
- Robust security: Saga Chainlets are secured by the Saga Mainnet validator mechanism through shared security.
- High performance: With parallel appchain versions, applications can achieve maximum performance and speed.
- Low and predictable gas fees: On private blockchains, users not only avoid unwanted gas fees from other applications but also have predictable block space.
- Fully automated: With Saga, obtaining dedicated block space is as easy as deploying smart contracts.
- Easy and fast interaction: Users can freely and quickly transfer assets between ecosystems through Saga’s automatic interaction capability and asynchronous combination.
- Fully flexible stack: Developers enjoy their dedicated blockchain, enabling a flexible and optimized environment.
- Excellent scalability: Saga’s infinite horizontal scalability means users will never encounter performance issues due to lack of block space.
Furthermore, Saga also has Saga Multiverse with a program built on Pegasus aimed at breaking down barriers in Web3, connecting creators, and developers more effectively.
ALSO CHECK: How to KYC on OEX Testnet And Swap
What is the SAGA Token?
After learning about what Saga is, let’s delve into the project’s token – SAGA.
Basic Information about SAGA Token
- Token name: Saga
- Ticker: SAGA
- Blockchain: Cosmos
- Contract: Updating…
- Token type: Updating…
- Total Supply: Updating…
- Circulating Supply: Updating…
Utility of SAGA Token
To deploy and operate Chainlets, developers will need to pay a subscription fee. This is similar to subscribing to a service or using a paid application, where users must pay a fixed fee for the right to use and enjoy the services.
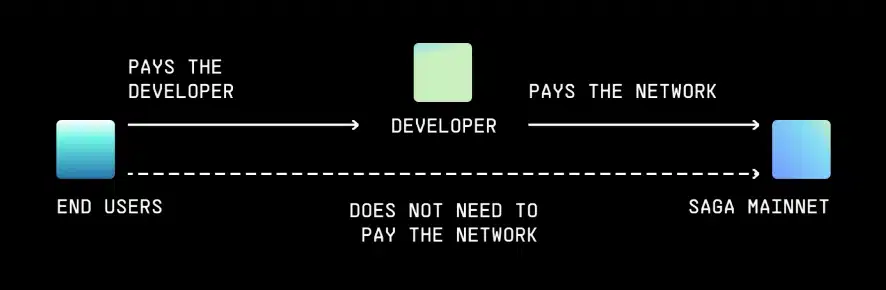
This subscription fee will be used to support validators, who ensure the security and stability of Chainlets. During operation, validators receive rewards as an incentive for their contribution to the ecosystem. This reward may be structured in the form of the project’s token or other formats depending on the system’s reward mechanism.
SAGA Protocol Airdrop – Saga Token Airdrop
Updating…
SAGA Token Allocation
Updating…
SAGA Token Release Schedule
Updating…
Buying and Selling SAGA Token
SEE HOW: I am Making ₦5000 ($10) Daily with Just My One Time Payment of ₦1000 ($2) RECOMMENDED: CLICK HERE to Start Now!!! DON'T MISS THIS
On April 9, 2024, Binance will list Saga on its platform. You can buy, sell, and store on this platform.
Roadmap
Q1 2024
- Mainnet Phase 1: Deployment of Security Chain and Token Generation Event (TGE)
- Mainnet Phase 2: Activation of Basic Cross-Chain Validation feature
- Mainnet Phase 3: Chainlets begin integrating security mechanisms from Saga
- Mainnet Phase 4, 5: Validators participate in transaction validation for Saga
- Mainnet Phase 6: Launch of Saga Protocol Version 1
- Mainnet Phase 7: Update of Saga Protocol Version 2
Q2 2024
- Mainnet 1 of Version 2 of Mainnet
- Mainnet 2 of Version 2 of Mainnet
Related: How to Start Celia Token Mining
Development Team

- Rebecca Liao – (CEO): Previously, she was a Co-founder and CEO of Skuchain, where she led the company to achieve annual revenues exceeding $5 billion. Currently, Rebecca is an Advisor to Sommelier Protocol, responsible for designing DAO to optimize governance, platform development, and regulatory compliance.
- Jacob McDorman – (CTO): He is an entrepreneur and researcher with over a decade of product development experience. He has a practical vision and approach, having been a startup founder, entrepreneur, studio owner, and advisor.
- Jin Kwon – (CSO): He has contributed to the Cosmos ecosystem since 2018 and currently holds several key positions at Tendermint. He has a diverse background in engineering, sales, marketing, and finance, aspiring to see web3 technology integrated widely into daily life.
- Bogdan Alexandrescu (Vice President, Engineering): He is a technology expert and industry leader with experience in various fields, from technology to fintech and business consulting. Prior to joining Saga, he had a notable career at Apple Inc and worked on large-scale projects in machine learning and artificial intelligence.
Investors
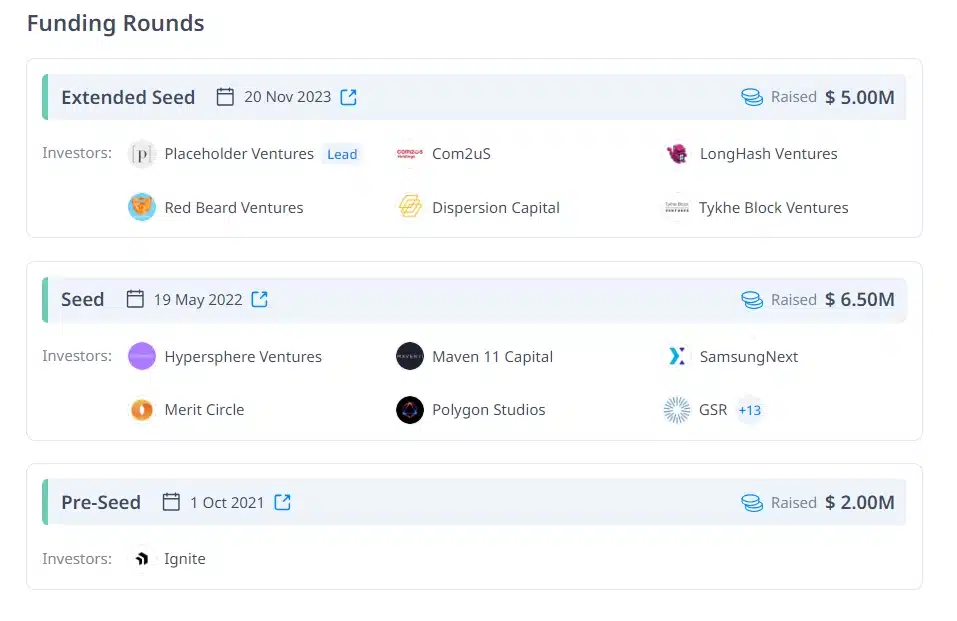
Saga has completed 3 seed funding rounds, with a total amount raised of $13.5 million. These funding rounds involved participation from investment funds and organizations such as Placeholder, Samsung Next, GSR, Longhash Ventures, Maven11, Hypersphere,…
Project Information
Conclusion
Above are some information about what Saga is? Investing also depends on many factors. And our article is only intended to provide knowledge, not investment advice
Join Me On My "YouTube Channel"
